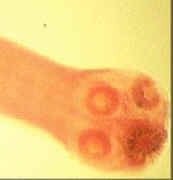
3. This structure which helps tapeworms attach inside the digestive system of the host and hold on is called a _____________.
PRACTICE SEMESTER TEST-ZOOLOGY
Classification & Intro to Animals
Chap 18 & 34
1. When writing the scientific name of an organism using binomial nomenclature you should always
capitalize
both names
underline the first but not the last
name
capitalize the first name only and
italicize or underline both
write the common name in parentheses
at the end
2.
In vertebrates the blastopore in the embryo becomes the ____________.
mouth anus gonads cladogram
Worms
Chap 36 & 37

3. This structure which helps tapeworms attach inside the digestive system of
the host and hold on is called a _____________.
proglottid tegument filaria scolex
4. The _____________ is the intermediate host of the blood fluke Schistosoma.
human snail cow pig
Mollusks
Chap 37
5. The respiratory organ in clams is the _______________.
lung gills skin gills Malpighian tubules
6. Bivalves ___________________________.
are sessile
most of their life
have 2 shells
do NOT have a
radula
All of the
above
Arthropods
Chap 38
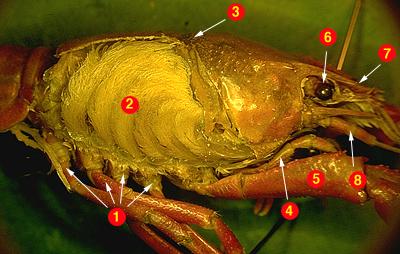
7. #2 is the ______________
digestive gland gills heart liver
8. Place where crayfish carry their eggs and young.
in
their cloaca
in their uterus
on their swimmerets
They don't carry their young; they hide them in weeds on the bottom
Echinoderms
Chap 40
9. Type of larva seen in echinoderms
bipinnaria nauplius trochopore echinoderms don't have larva
10. The name echinoderm means ______________________.
jointed
leg
changing
life
spiny skin
bony skeleton
Fish
Chap 41
11. The heart of a fish has _____________________.
1 atrium
and 1 ventricle
2 atria and 1 ventricles
2 atria and 2 ventricles
1 atrium and 2 ventricles
12. The _________________ part of the brain controls the internal organs.
cerebrum
cerebellum
medulla oblongata
optic lobes
Amphibians
Chap 42
13. The membrane that holds the digestive organs in place is the _________________.
duodenum
ileum
amplexus
mesentery
Reptiles
Chap 43
14. In _____________________ a female retains the growing embryo in her body nourishing it with a placenta until it is born.
oviparity ovoviviparity viviparity
15. The part of the turtle's shell that covers the dorsal surface of its body is the ______________.
plastron carapace amnion autotom
Birds
Chap 44
16. The ________________ in an amniotic egg stores nitrogen waste and serves as the embryo's "lung" by exchanging carbon dioxide and oxygen through the shell.
yolk sac chorion aminon allantois
17. 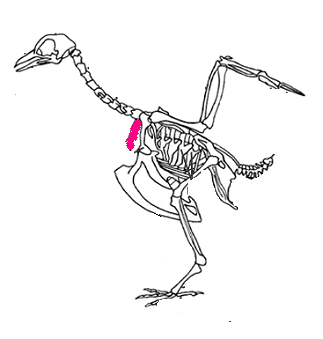
This colored bone is also called the "wishbone".
sternum furcula pygostyle syrinx
Mammals
Chap 45
18. _____________ would be an example of a monotreme.
playtypus walrus oppossum whale
19. T or
F All mammals are viviparous.
20. _______________ are streamlined, aquatic, carnivores with flippers.
marsupials monotremes cetaceans pinnepeds
GENERAL ANIMAL ?'s
21. Which of the following does NOT have a cloaca?
frog
turtle
pigeon rat
22. Which of the following animals belongs to the CLASS AVES?




23. TRUE or FALSE
Most invertebrates have a body plan
with a VENTRAL NERVE CORD and a DORSAL HEART and vertebrates have the opposite
(DORSAL NERVE CORD and VENTRAL HEART)
24. ALL chordates are DEUTEROSTOMES.
25. Name a group of animals you studied that are ENDOTHERMIC.
26. Name one of the types of coeloms you learned about and give an example of an animal that would have this type.
27. Name an organism you studied that does NOT have BILATERAL SYMMETRY.
28. Which of the following have external fertilization?
frog turtle pigeon rat
29. Name the 3 body systems that share the cloaca as an exit cavity.
30. TRUE or FALSE
ALL invertebrates are
PROTOSTOMES and ALL vertebrates are DEUTEROSTOMES.
31. Name the three kinds of reproduction you learned about.
32. Name an organism you learned about that doesn't use a kidney for excreting nitrogen waste and maintaining the ion/water balance.
33. Organism that has this kind of larva (nauplius).
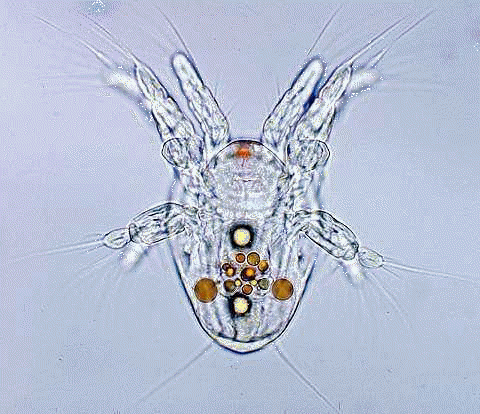 |
clam
crayfish starfish |
34. Name one of the animals you dissected and tell what organ it uses for respiration.
35. Name an animal you dissected that has open circulation.
ANSWERS:
1. capitalize the first name only and italicize or underline both
2. anus
3. scolex
4. snail
5. gills
6. all of the above
7. gills
8. on their swimmerets
9. bipinnaria
10. spiny skin
11. 1 atrium and 1 ventricle
12. medulla oblongata
13.mesentery
14. viviparity
15. carapace
16. allantois
17. furcula
18. platypus
19. false
20. pinnipeds
21. rat
22. owl (birds are AVES)
23. TRUE
24. TRUE (so are the Echinoderms)
25. birds OR mammals
26. Acoelom-flatworms
Pseudocoelom-
round worms
Eucoelom ("true") - segmented worms,
mollusks, echinoderms, arthropods, fish,
amphibians, reptiles, amphibians, birds, mammals
27. only one = starfish (echinoderms have radial symmetry)
28. frog
29. reproductive, digestive, excretory
30. FALSE; ALL vertebrates are deuterostomes; All invertebrates are
protostomes EXCEPT ECHINODERMS!
31. oviparity; ovoviviparity; viviparity
32. Earthworm; Arthropods (crayfish; spider; insects)
33. crayfish have nauplius larva;
clams have trochophore larva
echinoderms (starfish) have bipinnaria
34. earthworm-skin
clam, crayfish, fish -gills
starfish- none
frog- skin and lungs (gills as tadpole)
frog,turtle, bird, rat- lungs
35. clam or starfish (all the
others were closed)